📄 Assessing The Impact of CNN Auto Encoder-Based Image Denoising on Image Classification Tasks (https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.10664)
Abstract:
Images captured from the real world are often affected by different types of noise, which can significantly impact the performance of Computer Vision systems and the quality of visual data. This study presents a novel approach for defect detection in casting product noisy images, specifically focusing on submersible pump impellers. The methodology involves utilizing deep learning models such as VGG16, InceptionV3, and other models in both the spatial and frequency domains to identify noise types and defect status. The research process begins with preprocessing images, followed by applying denoising techniques tailored to specific noise categories. The goal is to enhance the accuracy and robustness of defect detection by integrating noise detection and denoising into the classification pipeline. The study achieved remarkable results using VGG16 for noise type classification in the frequency domain, achieving an accuracy of over 99%. Removal of salt and pepper noise resulted in an average SSIM of 87.9, while Gaussian noise removal had an average SSIM of 64.0, and periodic noise removal yielded an average SSIM of 81.6. This comprehensive approach showcases the effectiveness of the deep AutoEncoder model and median filter, for denoising strategies in real-world industrial applications. Finally, our study reports significant improvements in binary classification accuracy for defect detection compared to previous methods. For the VGG16 classifier, accuracy increased from 94.6% to 97.0%, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed noise detection and denoising approach. Similarly, for the InceptionV3 classifier, accuracy improved from 84.7% to 90.0%, further validating the benefits of integrating noise analysis into the classification pipeline.Proposed Auto-encoder model architecture:
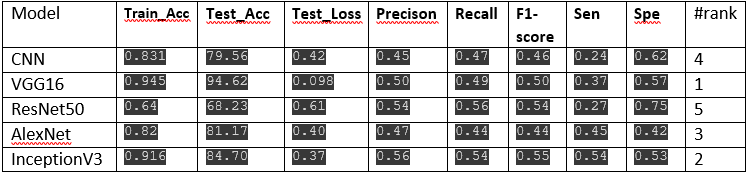
✅ Result of binary classification models:
Our metrics are: Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity, and F-1 Score
✅ Result of denoiser models :
Our metrics are: PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS
✅ Final lap: investigating the effect of noise on image classification models
Our metrics are: Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity, and F-1 Score
** 📄 Result: **
Periodic noise reduction (using autoencoder) -> PSNR= 26
Gaussian noise reduction (using autoencoder) -> PSNR= 28
salt and pepper noise reduction (using median filters) -> PSNR= 35
We have used the following deep learning models for image classification:
1️⃣ CNN – A baseline convolutional model for feature extraction.
2️⃣ VGG16 – A deep architecture with sequential convolutional layers.
3️⃣ AlexNet – A compact model designed for efficient classification.
4️⃣ ResNet50 – A residual network with 50 layers for improved accuracy.
5️⃣ Inception V3 – A deep architecture with multiple kernel sizes in parallel.
We applied deep learning-based noise detection and reduction techniques using:
- VGG16 – Used to classify different noise types from frequency domain representations.
-
Deep Autoencoder for Denoising 🌀
- A **fully convolutional autoencoder (with skip connections) ** was trained to remove Gaussian and periodic noise from images.
- The encoder compresses the noisy image into a low-dimensional latent space, removing noise-related information.
- The decoder reconstructs a denoised version of the image using transposed convolutions.
- A Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss is used to train the network, ensuring that the restored images remain as close as possible to their original noise-free versions.
-
Median Filter (Kernel Size = 3) 🏗️
- Applied for salt-and-pepper noise removal by replacing pixel values with the median of their neighborhood.
🔜 This repository will be updated with diffusion-based denoiser models for both image and speech domains to further enhance noise reduction capabilities! 🎤🖼️
Stay tuned for more improvements! ⭐
**Citation: **
@misc{hami2024assessing,
title={Assessing The Impact of CNN Auto Encoder-Based Image Denoising on Image Classification Tasks},
author={Mohsen Hami and Mahdi JameBozorg},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.10664},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}