Chatlaw: A Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Legal Assistant Enhanced by Knowledge Graph and Mixture-of-Experts.
-
Latest Version: Based on the InternLM architecture with a 4x7B Mixture of Experts (MoE) design.
-
Specialization: Tailored for Chinese legal language processing、
- Demo Version: Built on the Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1 model.
- Performance: Excels in general Chinese tasks but requires a larger model for complex legal QA.
- Demo Version: Utilizes the Anima-33B model.
- Enhancements: Improved logical reasoning over the 13B version.
- Challenge: Occasionally defaults to English responses due to limited Chinese training data in Anima.
- Function: A text similarity model trained on 93,000 court case decisions.
- Capability: Matches user queries to pertinent legal statutes, offering contextual relevance.
- Example: Connects questions about loan repayment to the appropriate sections of contract law.
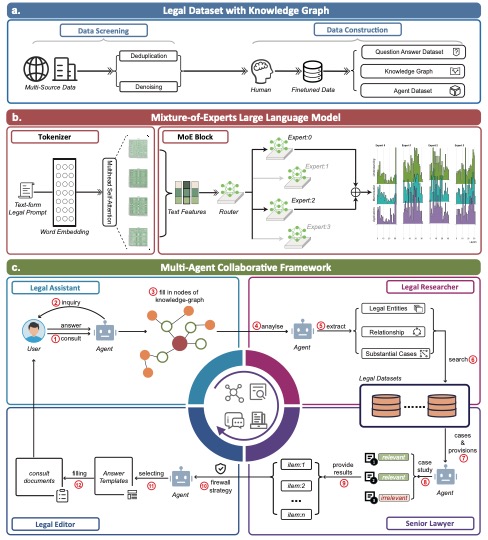
AI legal assistants, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), offer accessible legal consulting. However, the risk of hallucination in AI responses is a concern. This paper introduces ChatLaw, an innovative assistant that employs a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model and a multi-agent system to enhance reliability and accuracy in AI legal services. By integrating knowledge graphs and artificial screening, we've created a high-quality legal dataset for training the MoE model. This model leverages various experts to address a range of legal issues, optimizing legal response accuracy. Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs), inspired by law firm workflows, significantly minimize errors and hallucinations.
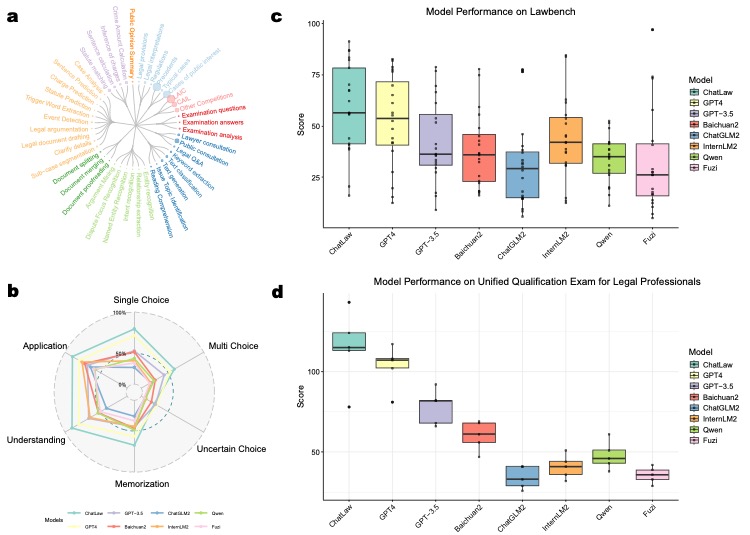
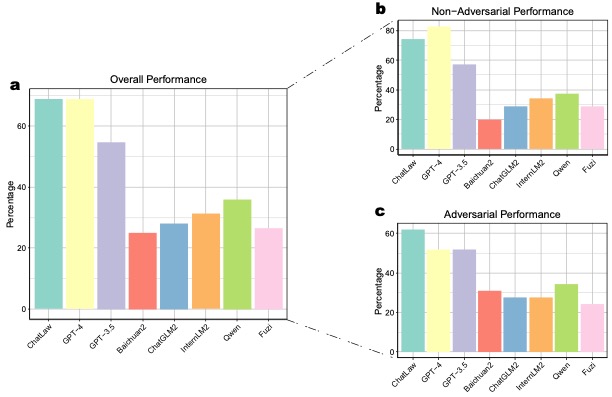
Our MoE model outperforms GPT-4 in the Lawbench and Unified Qualification Exam for Legal Professionals, achieving a 7.73% higher accuracy and an 11-point lead, respectively. It also surpasses other models in real-case consultations across multiple dimensions, showcasing robust legal consultation capabilities.
The diagram below illustrates the collaborative process of multiple agents in providing legal consultation services, exemplified by a divorce consultation. The process involves gathering information, legal research, comprehensive advice, and culminates in a detailed Legal Consultation Report.
(a) Our legal dataset covers a diverse range of tasks, from case classification to public opinion analysis.
(b) ChatLaw demonstrates superior performance across multiple legal categories compared to other models.
(c) ChatLaw consistently outperforms other models in legal cognitive tasks, as shown in the Lawbench comparison.
(d) ChatLaw maintains high performance across five years on the Unified Qualification Exam for Legal Professionals.
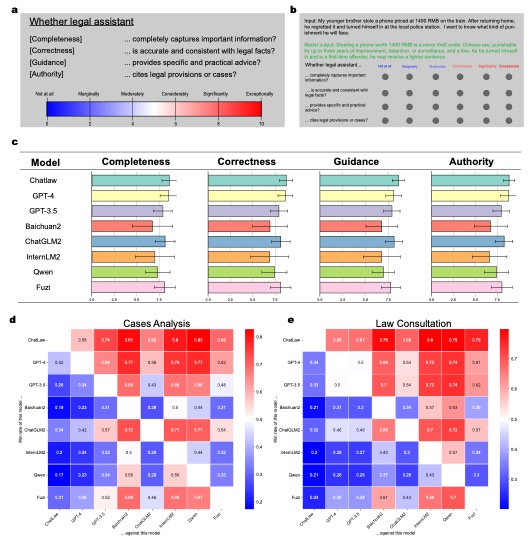
(a) Legal consultation quality is assessed based on Completeness, Logic, Correctness, Language Quality, Guidance, and Authority.
(b) ChatLaw achieves the highest scores across all criteria, particularly excelling in Completeness, Guidance, and Authority.
(c) ChatLaw shows a higher win rate compared to other models, indicating superior capability in providing high-quality legal consultations.
Find the model at: ChatLaw2-MoE
@misc{cui2024chatlaw,
title={Chatlaw: A Multi-Agent Collaborative Legal Assistant with Knowledge Graph Enhanced Mixture-of-Experts Large Language Model},
author={Jiaxi Cui and Munan Ning and Zongjian Li and Bohua Chen and Yang Yan and Hao Li and Bin Ling and Yonghong Tian and Li Yuan},
year={2024},
eprint={2306.16092},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
@misc{ChatLaw,
author={Jiaxi Cui and Zongjian Li and Yang Yan and Bohua Chen and Li Yuan},
title={ChatLaw},
year={2023},
publisher={GitHub},
journal={GitHub repository},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/ChatLaw}},
}