欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
本篇将给出三种C++实现的方法
- 数组模拟
- 双向队列模拟
- 直接分割链表
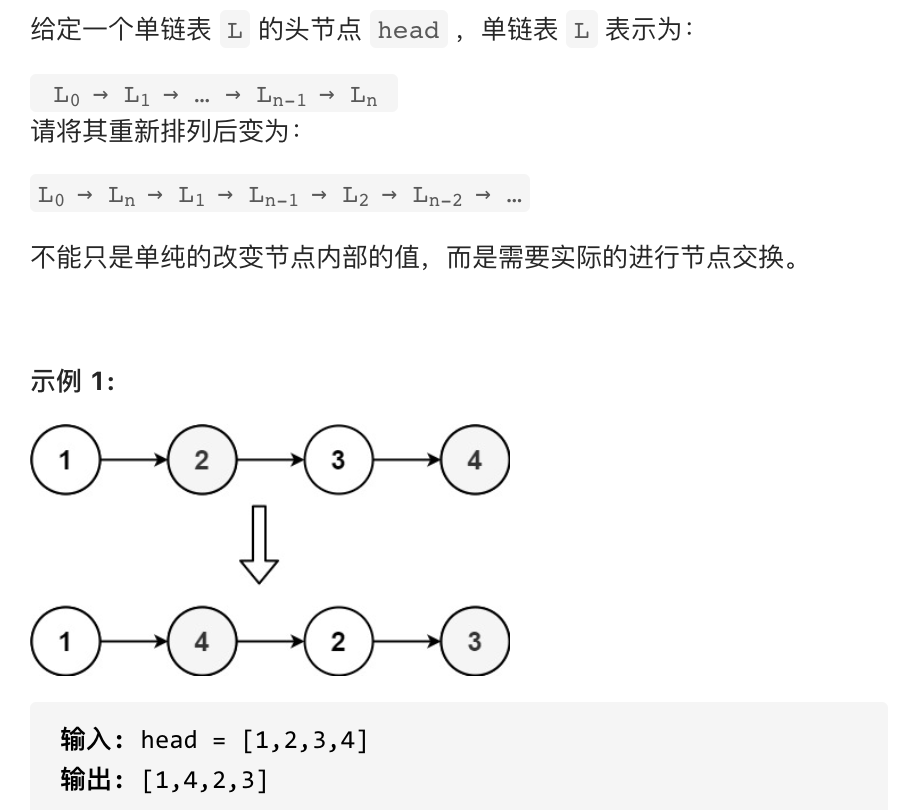
把链表放进数组中,然后通过双指针法,一前一后,来遍历数组,构造链表。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
vector<ListNode*> vec;
ListNode* cur = head;
if (cur == nullptr) return;
while(cur != nullptr) {
vec.push_back(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
int i = 1;
int j = vec.size() - 1; // i j为之前前后的双指针
int count = 0; // 计数,偶数去后面,奇数取前面
while (i <= j) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
cur->next = vec[j];
j--;
} else {
cur->next = vec[i];
i++;
}
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
if (vec.size() % 2 == 0) { // 如果是偶数,还要多处理中间的一个
cur->next = vec[i];
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = nullptr; // 注意结尾
}
};把链表放进双向队列,然后通过双向队列一前一后弹出数据,来构造新的链表。这种方法比操作数组容易一些,不用双指针模拟一前一后了
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
deque<ListNode*> que;
ListNode* cur = head;
if (cur == nullptr) return;
while(cur->next != nullptr) {
que.push_back(cur->next);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
int count = 0; // 计数,偶数去后面,奇数取前面
ListNode* node;
while(que.size()) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
node = que.back();
que.pop_back();
} else {
node = que.front();
que.pop_front();
}
count++;
cur->next = node;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = nullptr; // 注意结尾
}
};将链表分割成两个链表,然后把第二个链表反转,之后在通过两个链表拼接成新的链表。
如图:
这种方法,比较难,平均切割链表,看上去很简单,真正代码写的时候有很多细节,同时两个链表最后拼装整一个新的链表也有一些细节需要注意!
代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
// 反转链表
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur->next = pre; // 翻转操作
// 更新pre 和 cur指针
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return;
// 使用快慢指针法,将链表分成长度均等的两个链表head1和head2
// 如果总链表长度为奇数,则head1相对head2多一个节点
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next && fast->next->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* head1 = head;
ListNode* head2;
head2 = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
// 对head2进行翻转
head2 = reverseList(head2);
// 将head1和head2交替生成新的链表head
ListNode* cur1 = head1;
ListNode* cur2 = head2;
ListNode* cur = head;
cur1 = cur1->next;
int count = 0; // 偶数取head2的元素,奇数取head1的元素
while (cur1 && cur2) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
cur->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
} else {
cur->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
count++;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur2 != nullptr) { // 处理结尾
cur->next = cur2;
}
if (cur1 != nullptr) {
cur->next = cur1;
}
}
};Java:
// 方法三
public class ReorderList {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
//求出中点
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//right就是右半部分 12345 就是45 1234 就是34
ListNode right = slow.next;
//断开左部分和右部分
slow.next = null;
//反转右部分 right就是反转后右部分的起点
right = reverseList(right);
//左部分的起点
ListNode left = head;
//进行左右部分来回连接
//这里左部分的节点个数一定大于等于右部分的节点个数 因此只判断right即可
while (right != null) {
ListNode curLeft = left.next;
left.next = right;
left = curLeft;
ListNode curRight = right.next;
right.next = left;
right = curRight;
}
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode headNode = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = headNode.next;
headNode.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
return headNode.next;
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 方法一 Java实现,使用数组存储节点
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
// 双指针的做法
ListNode cur = head;
// ArrayList底层是数组,可以使用下标随机访问
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (cur != null){
list.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head; // 重新回到头部
int l = 1, r = list.size() - 1; // 注意左边是从1开始
int count = 0;
while (l <= r){
if (count % 2 == 0){
// 偶数
cur.next = list.get(r);
r--;
}else {
// 奇数
cur.next = list.get(l);
l++;
}
// 每一次指针都需要移动
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
// 当是偶数的话,需要做额外处理
if (list.size() % 2== 0){
cur.next = list.get(l);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 注意结尾要结束一波
cur.next = null;
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 方法二:使用双端队列,简化了数组的操作,代码相对于前者更简洁(避免一些边界条件)
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
// 使用双端队列的方法来解决
Deque<ListNode> de = new LinkedList<>();
// 这里是取head的下一个节点,head不需要再入队了,避免造成重复
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
de.offer(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head; // 回到头部
int count = 0;
while (!de.isEmpty()){
if (count % 2 == 0){
// 偶数,取出队列右边尾部的值
cur.next = de.pollLast();
}else {
// 奇数,取出队列左边头部的值
cur.next = de.poll();
}
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
cur.next = null;
}
}Python:
# 方法二 双向队列
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
d = collections.deque()
tmp = head
while tmp.next: # 链表除了首元素全部加入双向队列
d.append(tmp.next)
tmp = tmp.next
tmp = head
while len(d): # 一后一前加入链表
tmp.next = d.pop()
tmp = tmp.next
if len(d):
tmp.next = d.popleft()
tmp = tmp.next
tmp.next = None # 尾部置空
# 方法三 反转链表
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
if head == None or head.next == None:
return True
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
right = slow.next # 分割右半边
slow.next = None # 切断
right = self.reverseList(right) #反转右半边
left = head
# 左半边一定比右半边长, 因此判断右半边即可
while right:
curLeft = left.next
left.next = right
left = curLeft
curRight = right.next
right.next = left
right = curRight
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
pre = None
while(cur!=None):
temp = cur.next # 保存一下cur的下一个节点
cur.next = pre # 反转
pre = cur
cur = temp
return preGo:
JavaScript: