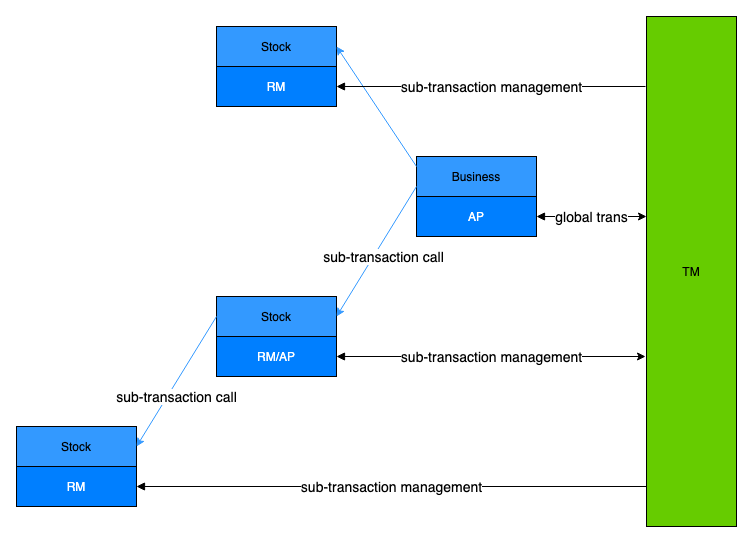
A dtm transaction has three roles:
- RM-Resource Manager: Manage system resources. The database is a resource manager that handles management resources and should also have the ability to manage transaction commit and rollback.
- RM manages sub-transactions in distributed transactions, and is responsible for operations such as modification, submission, rollback, and compensation of related data. Usually corresponds to a microservice.
- TM-Transaction Manager: The transaction manager is the core manager of distributed transactions. The transaction manager communicates with each RM (Resource Manager) to coordinate and complete transaction processing.
- Every global transaction is registered in TM, and every sub-transaction is also registered in TM. TM will coordinate all RMs, commit all different sub-transactions of the same global transaction, or roll back all of them.
- AP-Application Program: The application program calls the RM interface according to the business rules to complete the changes to the business model data.
- The AP will register the global transaction, register the sub-transactions according to the business rules, and call the RM interface. Usually corresponds to a microservice.
In the case of nested sub-transactions, a microservice will play the roles of RM and AP at the same time, as shown in the figure
Currently dtm only supports the http protocol. Since distributed transactions involve the collaboration of multiple roles, some participants may be temporarily unavailable and need to be retried; some participants clearly inform that they have failed and need to be rolled back.
The following is a classification description of each situation, and the return value of each situation is defined. The design mainly draws on the interface of WeChat/Alipay order success callback. They also return SUCCESS to indicate success and do not retry.
In the above figure, there are mainly the following types of interfaces:
AP calls the TM interface, mainly for global transaction registration, submission, and sub-transaction registration, etc.:
- Success: { dtm_result: "SUCCESS" }
- Failure: { dtm_result: "FAILURE" }, indicates that the status of this request is incorrect, for example, a failed global transaction is not allowed to register branches.
- Other errors need to be tried again.
TM calls the RM interface, mainly for the two-phase commit, rollback, and each branch of saga
- Success: { dtm_result: "SUCCESS" }, indicates that this interface is successfully called, and proceed to the next step normally.
- Failure: { dtm_result: "FAILURE" }, indicates that this interface call failed and the business needs to be rolled back. For example, if the action in saga returns FAILURE, the entire saga transaction fails and rolls back.
- Others need to retry (The result is uncertain, need to retry).
AP calls the RM interface, which is related to the business, and the recommended interface form (not required):
- Success: { dtm_result: "SUCCESS" }, indicates that this interface is successfully called, and proceed to the next step normally. The returned result can also contain other business data.
- Failure: { dtm_result: "FAILURE" }, indicates that this interface call failed and the business needs to be rolled back. For example, if the Try action in tcc returns FAILURE, the entire tcc transaction fails and rolls back.
- Others need to retry (The result is uncertain, need to retry).