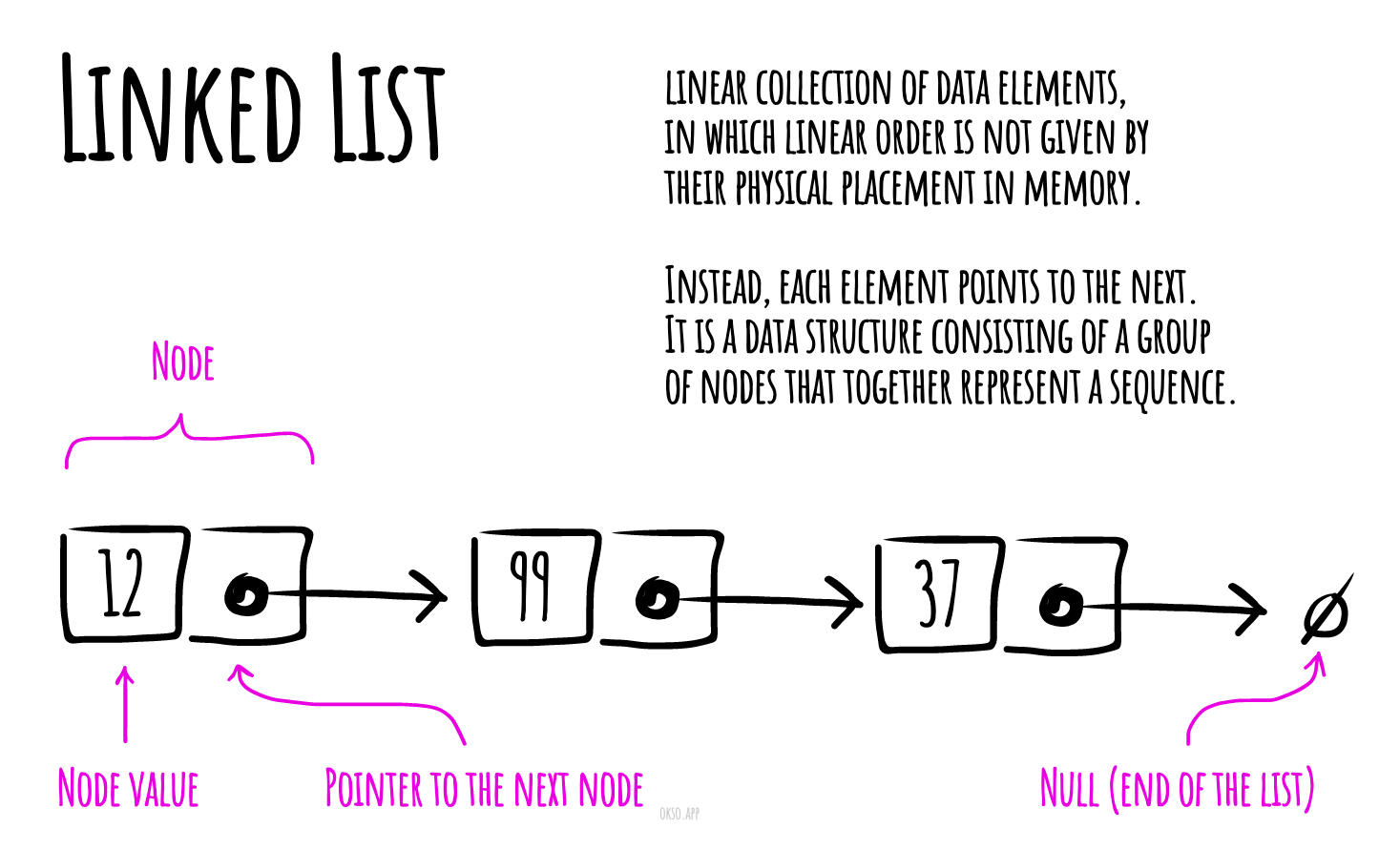
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements, in which linear order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration.
Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have the following limitations:
- The size of the array is fixed: We must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage.
- Insertion of a new element/deletion of an existing element in an array of elements is expensive: The room has to be created for the new elements and to create room, so existing elements have to be shifted. But in Linked list, if we have the head node then we can traverse to any node through it and insert new node at the required position.
- Dynamic array.
- Ease of insertion or deletion.
- Random access is not allowed. We have to access elements sequentially starting from the first node(head node). So we cannot do a binary search with linked lists efficiently with its default implementation.
- Extra memory space for a pointer is required with each element of the list.
- It takes a lot of time in traversing and changing the pointers.
- Reverse traversing is not possible in singly linked lists.
- Direct access to an element is not possible in a linked list as in an array by index.
- Searching for an element is costly and requires O(n) time complexity.
- Sorting of linked lists is very complex and costly.
- Simple Linked List: In this type of linked list, one can move or traverse the linked list in only one direction. where the next pointer of each node points to other nodes but the next pointer of the last node points to NULL. It is also called “Singly Linked List”.
- Doubly Linked List: In this type of linked list, one can move or traverse the linked list in both directions (Forward and Backward).
- Circular Linked List: In this type of linked list, the last node of the linked list contains the link of the first/head node of the linked list in its next pointer.
- Doubly Circular Linked List: A Doubly Circular linked list or a circular two-way linked list is a more complex type of linked list that contains a pointer to the next as well as the previous node in the sequence. The difference between the doubly linked and circular doubly list is the same as that between a singly linked list and a circular linked list. The circular doubly linked list does not contain null in the previous field of the first node.
- Insertion.
- Deletion.
- Search.
- Display.