Swiper component for React Native with previews, snapping effect and RTL support. Compatible with Android & iOS. Pull requests are very welcome!
- Showcase
- Breaking change
- Usage
- Props
- Methods
- Properties
- Example
- Tips and tricks
- RTL support
- ScrollView's limitations
- TODO
- Credits
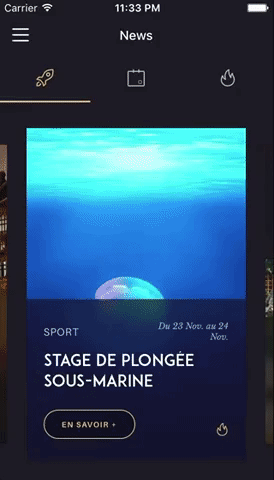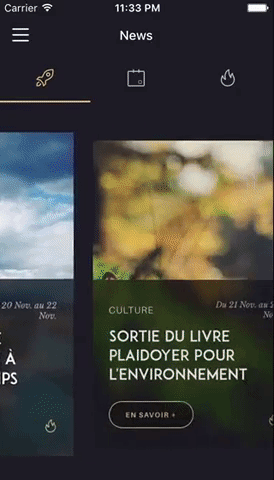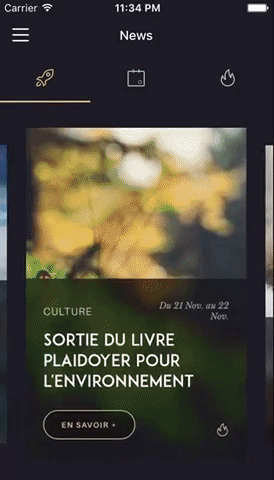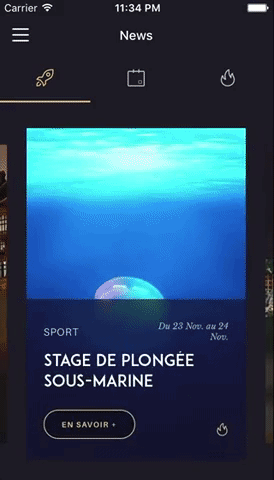
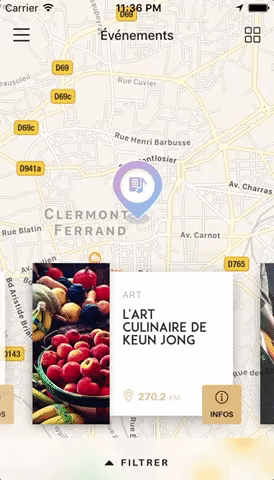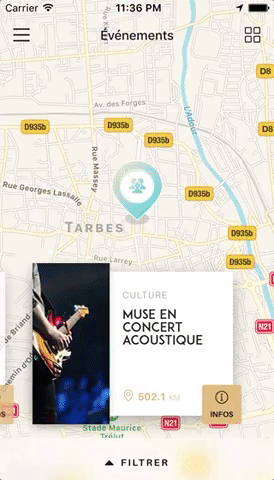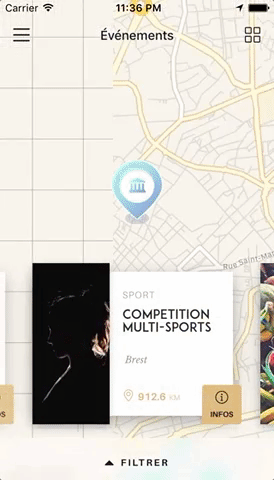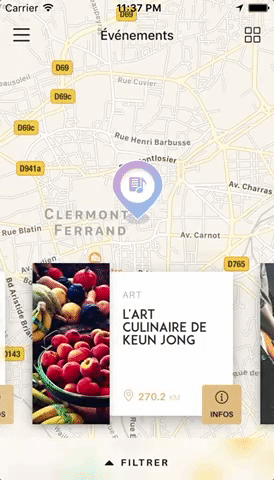
You can try these examples live in Archriss' showcase app on Android and iOS.
Since it has been asked multiple times, please note that we do not plan on Open-Sourcing the code of our showcase app. Still, we've put together an example for you to play with, and you can find some insight about our map implementation in this comment.
App currently uses version 1.4.0 of the plugin. Especially, this means that you should expect slider's layout to break with RTL devices (see #38) since support was added in version 2.1.0.
Since version 2.0.0, items are now direct children of the component. As a result, props items and renderItem have been removed.
$ npm install --save react-native-snap-carousel
import Carousel from 'react-native-snap-carousel';
// Example with different children
render () {
return (
<Carousel
ref={(carousel) => { this._carousel = carousel; }}
sliderWidth={sliderWidth}
itemWidth={itemWidth}
>
<View style={styles.slide1} />
<Text style={styles.slide2} />
<Image style={styles.slide3} />
</Carousel>
);
}
// Example of appending the same component multiple times while looping through an array of data
render () {
const slides = this.state.entries.map((entry, index) => {
return (
<View key={`entry-${index}`} style={styles.slide}>
<Text style={styles.title}>{ entry.title }</Text>
</View>
);
});
return (
<Carousel
ref={(carousel) => { this._carousel = carousel; }}
sliderWidth={sliderWidth}
itemWidth={itemWidth}
>
{ slides }
</Carousel>
);
}| Prop | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| itemWidth | Width in pixels of carousel's items, must be the same for all of them | Number | Required with horizontal carousel |
| itemHeight | Height in pixels of carousel's items, must be the same for all of them | Number | Required with vertical carousel |
| sliderWidth | Width in pixels of the carousel itself | Number | Required with horizontal carousel |
| sliderHeight | Height in pixels of the carousel itself | Number | Required with vertical carousel |
| Prop | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| activeSlideOffset | From slider's center, minimum slide distance to be scrolled before being set to active | Number | 25 |
| enableMomentum | See momentum. Warning: this prop can't be changed dynamically. | Boolean | false |
| enableSnap | If enabled, releasing the touch will scroll to the center of the nearest/active item. Warning: this prop can't be changed dynamically. | Number | true |
| firstItem | Index of the first item to display | Number | 0 |
| scrollEndDragThrottleValue | When momentum is disabled, this throttle helps smoothing slides' snapping by providing a bit of inertia when touch is released. Note that this will delay callback's execution. | Number | 50 for iOS, 150 for Android |
| shouldOptimizeUpdates | Whether to implement a shouldComponentUpdate strategy to minimize updates |
Boolean | true |
| snapCallbackDebounceValue | This defines the timeframe during which multiple callback calls should be "grouped" into a single one. Note that this will delay callback's execution. | Number | 250 |
| snapOnAndroid | Snapping on android is kinda choppy, especially when swiping quickly so you can disable it. Warning: this prop can't be changed dynamically. | Boolean | true |
| swipeThreshold | Delta x when swiping to trigger the snap | Number | 20 |
| vertical | Layout slides vertically instead of horizontally | Boolean | false |
| Prop | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| autoplay | Trigger autoplay on mount. Warning: this prop can't be changed dynamically. | Boolean | false |
| autoplayDelay | Delay before enabling autoplay on startup & after releasing the touch | Number | 5000 |
| autoplayInterval | Delay in ms until navigating to the next item | Number | 3000 |
| Prop | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| animationFunc | Animated animation to use. Provide the name of the method | String | timing |
| animationOptions | Animation options to be merged with the default ones. Can be used w/ animationFunc | Object | { easing: Easing.elastic(1) } |
| carouselHorizontalPadding | Override container's inner horizontal padding (needed for slides's centering in a horizontal carousel). Warning: be aware that overriding the default value can mess with carousel's behavior. | Number | (sliderWidth - itemWidth) / 2 |
| carouselVerticalPadding | Override container's inner vertical padding (needed for slides's centering in a vertical carousel). Warning: be aware that overriding the default value can mess with carousel's behavior. | Number | (sliderHeight - itemHeight) / 2 |
| containerCustomStyle | Optional styles for Scrollview's global wrapper | ScrollView Style Object | {} |
| contentContainerCustomStyle | Optional styles for Scrollview's items container | ScrollView Style Object | {} |
| inactiveSlideOpacity | Value of the opacity effect applied to inactive slides | Number | 1 |
| inactiveSlideScale | Value of the 'scale' transform applied to inactive slides | Number | 0.9 |
| slideStyle | Optional style for each item's container (the one whose scale and opacity are animated) | Animated View Style Object | {} |
| Prop | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| onLayout(event) | Exposed View callback; invoked on mount and layout changes |
Function | undefined |
| onScroll(event) | Exposed ScrollView callback; fired while scrolling |
Function | undefined |
| onScrollViewScroll(event) | Callback fired while scrolling (deprecated: use onScroll instead) |
Function | undefined |
| onSnapToItem(slideIndex) | Callback fired when navigating to an item | Function | undefined |
In addition to these props, you can use any prop from the ScrollView component.
Here are a few useful ones: removeClippedSubviews, showsHorizontalScrollIndicator, overScrollMode (android), bounces (ios), decelerationRate (ios), scrollEventThrottle (ios).
In order to use the following methods, you need to create a reference to the carousel's instance. There are two ways of doing it.
<Carousel
// other props
ref={(carousel) => { this._carousel = carousel; }}
/>
// methods can then be called this way
onPress={() => { this._carousel.snapToNext(); }}ref as a string attribute (legacy)
<Carousel
// other props
ref={'carousel'}
/>
// methods can then be called this way
onPress={() => { this.refs.carousel.snapToNext(); }}startAutoplay (instantly = false)Start the autoplay manuallystopAutoplay ()Stop the autoplay manuallysnapToItem (index, animated = true)Snap to an item manuallysnapToNext (animated = true)Snap to next item manuallysnapToPrev (animated = true)Snap to previous item manually
You need a reference to the carousel's instance (see above if needed).
currentIndexCurrent active item (int, starts at 0)
You can find the following example in the /example folder.
Since 1.5.0, the snapping effect can now be based on momentum instead of when you're releasing your finger. It means that the component will wait until the ScrollView isn't moving anymore to snap. By default, the inertia isn't too high on Android. However, we had to tweak the default iOS value a bit to make sure the snapping isn't delayed for too long.
You can adjust this value to your needs thanks to this prop.
Make also sure to play with the props scrollEndDragThrottleValue and snapCallbackDebounceValue; they can help achieving a better snap feeling, especially when momentum is disabled.
As a rule of thumb, we recommend setting
enableMomentumtofalse(default) anddecelerationRateto'fast'when you are displaying only one main slide (as in the showcase above), and to usetrueand0.9otherwise.
If you need some extra horizontal margin between slides (besides the one resulting from the scale effect), you should add it as paddingHorizontal on slide's container. Make sure to take this into account when calculating item's width.
const horizontalMargin = 20;
const slideWidth = 280;
const sliderWidth = Dimensions.get('window').width;
const itemWidth = slideWidth + horizontalMargin * 2;
const itemHeight = 200;
const styles = Stylesheet.create({
slide: {
width: itemWidth,
height: itemHeight
// other styles for your item's container
}
};
return (
<Carousel
sliderWidth={sliderWidth}
itemWidth={itemWidth}
>
<View style={styles.slide} />
<View style={styles.slide} />
<View style={styles.slide} />
</Carousel>
);Here is a screenshot that should help you understand how each of the above variables is used.
Since version 2.2.0, slides will re-center properly if you update slider and/or items's dimensions when onLayout is fired.
Here is an example of a working implementation (thanks @andrewpope):
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
viewport: {
width: Dimensions.get('window').width,
height: Dimensions.get('window').height
}
};
}
render() {
return (
<View
onLayout={() => {
this.setState({
viewport: {
width: Dimensions.get('window').width,
height: Dimensions.get('window').height
}
});
}}
>
<Carousel
ref={carousel => { this.carousel = carousel; } }
sliderWidth={this.state.viewport.width}
itemWidth={this.state.viewport.width}
...
>
</Carousel>
</View>
);
}
While the plugin hasn't been designed with this use case in mind, you can easily implement fullscreen slides. The following code should serve as a good starting point.
const { width: viewportWidth, height: viewportHeight } = Dimensions.get('window');
return (
<Carousel
sliderWidth={viewportWidth}
itemWidth={viewportWidth}
slideStyle={{ width: viewportWidth }}
inactiveSlideOpacity={1}
inactiveSlideScale={1}
>
<View style={{ height: viewportHeight }} /> // or { flex: 1 } for responsive height
<View style={{ height: viewportHeight }} /> // or { flex: 1 } for responsive height
<View style={{ height: viewportHeight }} /> // or { flex: 1 } for responsive height
</Carousel>
);You might encounter the following error when using the plugin in conjonction with Jest: TypeError: Cannot read property 'style' of undefined at Object.<anonymous>.
As you can see here, this is because React Native mocks ScrollView for you when you write unit tests with Jest.
The easiest workaround is to add jest.unmock('ScrollView') before importing the component in your test file (thanks @hoangnm for the tip!).
Since version 2.1.0, the plugin is compatible with RTL layouts. Our implementation relies on miscellaneous hacks that work around a React Native bug with horizontal ScrollView.
As such, this feature should be considered experimental since it might break with newer versions of React Native.
There is one kown issue with RTL layouts: during init, the last slide will shortly be seen. You can work around this by delaying slider's visibility with a small timer (FYI, version 0.43.0 of React Native introduced a display style prop that could either be set to flex or none).
Note that this plugin is built on top of React Native's ScrollView. Unfortunately, its implementation shows flaws that affect the plugin, the main ones being the following:
- there is no
onScrollEndevent scrollTomethod doesn't accept any callback- Android's
scrollToanimation is quite brutal.
We're trying to work around these issues, but the result is not always as smooth as we'd want it to be. Keep that in mind and go spam React Native's Feature Request ;-)
- Implement 'loop' mode
- Implement 'preload' mode
- Handle changing props on-the-fly
- Handle autoplay properly when updating children's length
- Add vertical implementation
- Handle device orientation event (see [this note] (https://github.com/archriss/react-native-snap-carousel#handling-device-rotation))
- Add RTL support
- Improve momemtum handling
- Improve snap on Android
- Handle passing 1 item only
- Fix centering
Written by Maxime Bertonnier and Benoît Delmaire at Archriss.