A command-line tool that can encode a file to an image and can decode encoded output back to its original version.
- This tool aims to support encoding & decoding operations for all ASCII characters.
- Each pixel in the encoded image encodes a single character in the input string.
- Since each pixel has 3 components in an RGB image, encoding a single ASCII character can be thought as converting a decimal number to a number system with base n, where the encoded version contains exactly 3 digits, and the decimal number to be converted is in the interval [0, 255]. The minimum value for n is 7 since 63 = 216 (insufficient), whereas 73 = 343 (sufficient). Similarly, decoding the encoded RGB pixel can be thought as converting a base-n number to the decimal number system.
- 7 different color intensity values, each of which is in the interval [0, 255], is randomly generated.
- Since the color intensity values are randomly generated, the same input is encoded to different images, with a very low probability of resulting in the same image, at each run. Each of those different images are successfully decoded to the original input since the encoding and decoding processes are based on the ascending order of the different color intensity values in the image, not directly on the values of the color intensity values.
- The generated color intensity values are sorted in ascending order, and each color intensity value is mapped to a number from 0 to 6 according to its rank (e.g., The smallest color intensity value represents the number 0, whereas the greatest color intensity value represents the number 6.).
- For each of characters in the input string, the decimal value (according to the ASCII table) of the character is converted to base-7 number system, and the resulting 3-digit base-7 number is converted to its RGB pixel representation by using the mapping mentioned above.
- All different color intensity values used in the image is detected. The number of different color intensity values indicates what base is used in encoding process. (e.g., if there are 7 different color intensity values in the overall image, which is the case for this tool, this means that base-7 number system has been used in encoding operation.)
- The detected color intensity values are sorted in ascending order, and each color intensity value is mapped to a number from 0 to 6 according to its rank, just as in the encoding operation.
- For each pixel in the input image, the RGB pixel value is first converted to the base-7 number represented by the pixel by using the mapping mentioned above. Then, the resulting 3-digit base-7 number is converted to decimal number system. As the last step, the character representation of the decimal number (according to the ASCII table) is obtained.
- Python>=3.6
- opencv-python: https://pypi.org/project/opencv-python/
- numpy: https://pypi.org/project/numpy/
-
To encode the input file:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i <input_path> -o <output_path>
-
To encode the input file using base64 encoding:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i <input_path> -o <output_path> -b64
- To encode binary files, using -b64 is compulsory.
- Text files can also be encoded using -b64 option.
- Using -b64 option is recommended for all types of files.
- When -b64 is used in encoding operation, the binary content of the input file is first encoded using base64; then, base64-encoded string is encoded into an image.
-
To decode the input file:
python3 Main.py -op decode -i <input_path> -o <output_path>
-
To decode the input file using base64 encoding:
python3 Main.py -op decode -i <input_path> -o <output_path> -b64
- -b64 option is used while decoding if and only if the encoded input file was encoded using base64.
- When -b64 is used in decoding operation, the base64-encoded string obtained by decoding the input image is decoded using base64. Then, the binary result is written to the output file.
-
Extension of the encoded image file is determined by the output filename specified by the user in the command. Using extensions other than .png in encoded image may cause unexpected behavior. Therefore, using .png extension for encoded image is recommended.
-
Command:
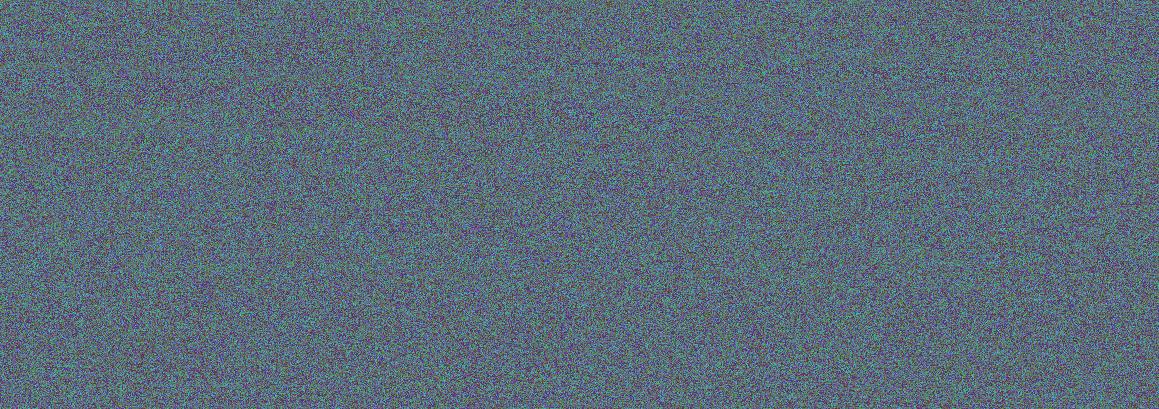
python3 Main.py -op encode -i input.txt -o text_output.png
-
Output:
-
Command:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i input.txt -o text_output2.png
-
Output:
-
Command:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i input.txt -o text_output3.png
-
Output:
-
Command:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i input2.png -o binary_output.png -b64
-
Output:
-
Command:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i input2.png -o binary_output2.png -b64
-
Output:
-
Command:
python3 Main.py -op encode -i input2.png -o binary_output3.png -b64
-
Output:
python3 Main.py -op decode -i text_output.png -o output.txt
python3 Main.py -op decode -i binary_output.png -o output.png -b64